Electric Circuits Tutoring: Tips, Techniques, and Tools for Success
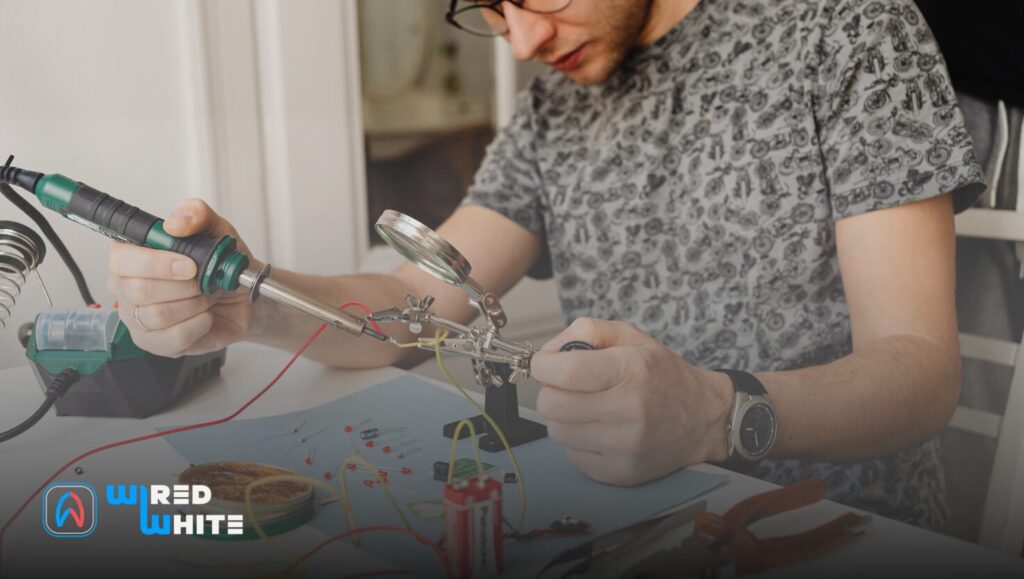

Introduction to Electric Circuits Tutoring
Electric circuits are the backbone of modern technology. From powering household appliances to enabling sophisticated robotics, understanding how electric currents flow is essential for anyone venturing into electronics or engineering. However, the concepts can be complex and intimidating for students, which is where electric circuits tutoring comes in. Personalized tutoring helps bridge the gap between theory and practice, making abstract concepts tangible and easier to grasp.
Whether you’re a high school student tackling basic circuits or a university engineering student navigating complex AC and DC networks, tutoring offers structured guidance and hands-on learning experiences. Think of a tutor as a GPS for the intricate maze of resistors, capacitors, and inductors — guiding you smoothly from confusion to mastery.
What is an Electric Circuit?
At its core, an electric circuit is a closed path through which electric current flows. It consists of several components:
- Voltage source: Powers the circuit (like batteries or generators)
- Conductors: Wires that allow current to flow
- Load: Devices or components that consume electricity (resistors, bulbs, motors)
- Switches: Control the flow of electricity
Types of Electric Circuits
Series Circuits: Components connected in a single path. If one component fails, the entire circuit stops.
Parallel Circuits: Components connected across multiple paths, allowing current to flow through more than one branch.
Combination Circuits: Mix of series and parallel components, often used in complex systems.

Why Students Struggle with Electric Circuits
Understanding electric circuits requires grasping both theory and practical application. Common hurdles include:
- Complexity: Circuits often involve multiple components and calculations.
- Misconceptions: Students may confuse voltage, current, and resistance.
- Lack of hands-on experience: Reading theory alone is insufficient; experimentation is crucial.
Benefits of Electric Circuits Tutoring
Personalized Learning
Tutoring allows lessons to be tailored to individual strengths and weaknesses. No more generic class pace — you learn at your own speed.
Improved Conceptual Understanding
Tutors break down difficult topics into simple steps, making concepts like Kirchhoff’s laws and Ohm’s law more intuitive.
Hands-On Learning
Practical experiments solidify understanding. Tutors guide students in building real circuits or using simulation software, turning abstract numbers into observable results.
Choosing the Right Tutor
Qualifications to Look For
An ideal tutor has formal education in electrical engineering or electronics and experience teaching students at your level.
Teaching Style and Methods
Do they explain concepts clearly, use analogies, or provide visual aids? These qualities are crucial for comprehension.
Experience with Labs
A tutor who can guide you through hands-on experiments ensures you don’t just memorize formulas but understand real-world applications.
Find your perfect WiredWhite Electric Circuits tutors.
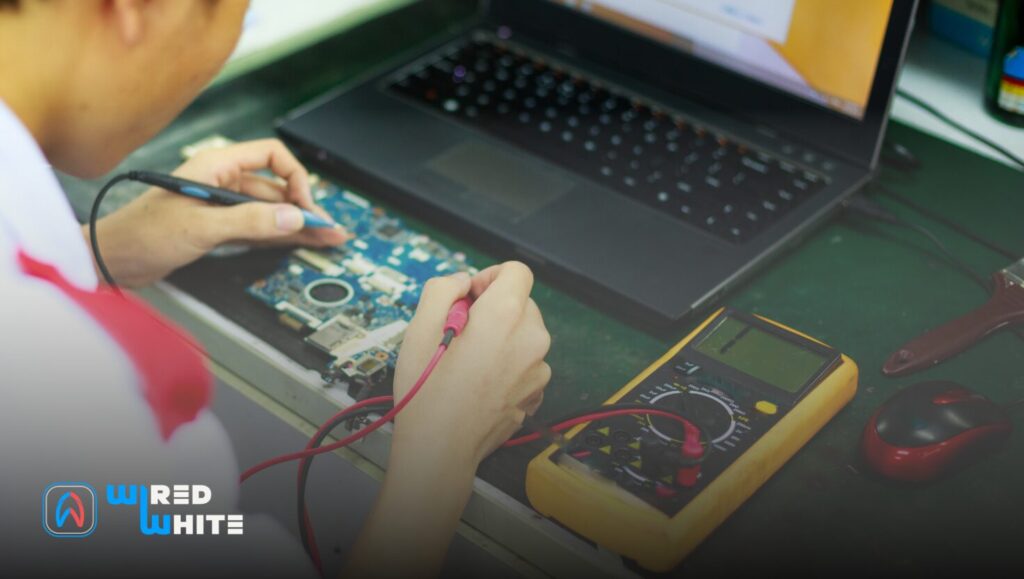

Core Topics Covered in Electric Circuits Tutoring
Ohm’s Law
This fundamental principle defines the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance — the cornerstone of all circuit analysis. Through practical examples and problem-solving exercises, you’ll learn how to apply Ohm’s Law to real systems, from simple LED circuits to complex power grids.
Kirchhoff’s Laws
Kirchhoff’s Current Law (KCL) and Voltage Law (KVL) are essential for understanding how electric charge and energy move within a circuit. Students learn to apply these laws to predict circuit behavior, solve network equations, and ensure designs are both efficient and safe.
AC and DC Circuits
Alternating Current (AC) and Direct Current (DC) circuits form the backbone of electrical systems — from household outlets to digital electronics. Tutoring sessions explain how these two types of circuits differ in behavior, design, and application, with hands-on examples involving rectifiers, transformers, and power supplies.
Resistors, Capacitors, and Inductors
These passive components are the building blocks of every electronic system. You’ll explore how resistors control current, capacitors store charge, and inductors manage magnetic energy. Detailed lessons cover their formulas, time constants, and frequency responses in both AC and DC environments.
Power and Energy Calculations
Understanding how to measure, manage, and optimize power is critical for real-world engineering. You’ll learn how to calculate energy consumption, power loss, and efficiency across different types of circuits — key skills for careers in electrical design, renewable energy, and embedded systems.
Circuit Analysis Tools and Simulation
In addition to theory, modern tutoring often includes training in circuit simulation software such as Multisim, LTSpice, or MATLAB. This allows students to visualize current flow, test virtual circuits, and develop strong analytical intuition before moving to physical experiments.
Real-Life Applications of Electric Circuits Knowledge
Electronics and Gadgets
Every modern electronic device — from smartphones and laptops to smart TVs and kitchen appliances — is powered by intricate electric circuits. Understanding how current flows and components interact allows engineers to design faster, safer, and more energy-efficient technology that improves everyday life.
Renewable Energy Systems
Electric circuits are at the heart of clean energy technologies. Solar panels, wind turbines, and battery storage systems all rely on precise circuit design to convert, regulate, and distribute power efficiently. Mastering circuit theory opens doors to careers in sustainable energy and green innovation.
Robotics and Automation
Robots move, sense, and respond thanks to carefully designed electronic circuits. Whether it’s a robotic arm assembling products or an autonomous drone navigating terrain, electric circuits control every movement and feedback signal. Engineers skilled in this field shape the future of manufacturing, healthcare, and artificial intelligence.
Automotive Electronics
Today’s vehicles are essentially computers on wheels. Circuits manage everything from engine performance and safety sensors to infotainment and electric drivetrains. With the rise of electric and autonomous vehicles, circuit expertise is in high demand among automotive engineers and system designers.
Smart Infrastructure and IoT (Internet of Things)
Modern cities depend on interconnected devices — from smart lighting and surveillance systems to home automation. Electric circuits enable seamless communication and energy efficiency across these systems, building the foundation for smarter and more sustainable urban environments.
Career Opportunities After Mastering Electric Circuits
Electrical Engineer
Electrical engineers design, test, and maintain power systems, control networks, and electronic equipment that keep modern life running — from renewable energy grids to electric vehicles. With strong circuit knowledge, you can work in energy, manufacturing, or technology sectors.
💰 Average salary: $75,000–$120,000 per year, depending on experience and industry.
Electronics Technician
Technicians play a hands-on role in assembling, troubleshooting, and improving electronic systems — from consumer devices to industrial automation tools. It’s a great career for those who enjoy practical problem-solving and working directly with hardware.
💰 Average salary: $45,000–$70,000 per year.
Research and Development (R&D) Engineer
If innovation excites you, R&D offers the chance to push boundaries in robotics, telecommunications, renewable energy, and smart technologies. You’ll prototype circuits, experiment with new materials, and develop future-ready systems.
💰 Average salary: $80,000–$130,000 per year.
Teaching and Tutoring
For those passionate about sharing knowledge, teaching offers the opportunity to mentor students in universities, colleges, or online platforms. Educators in this field often combine academic insight with real-world engineering experience.
💰 Average salary: $40,000–$85,000 per year, with higher earnings possible for experienced professors or private tutors.
Conclusion
Electric circuits tutoring transforms a challenging subject into an accessible, engaging experience. By combining theory with practical exercises, students gain confidence and competence, preparing them for academic success and real-world applications. Whether online, in-person, or hybrid, the right tutoring approach empowers learners to understand, experiment, and excel in electrical circuits.
FAQs
- How long does it take to understand electric circuits with tutoring?
Typically, 3–6 months of consistent sessions can provide a strong foundational understanding. - Do I need prior knowledge before starting tutoring?
No, tutors can start from basic concepts and build up gradually. - Can online tutoring be as effective as in-person sessions?
Yes, especially when combined with hands-on kits and simulation software. - What tools do I need for practicing at home?
Basic multimeter, breadboard, wires, resistors, and access to simulation software. - How can I apply what I learn in real-life projects?
By building small electronics projects, participating in robotics clubs, or creating DIY circuits for home gadgets.









Responses