Parametric Sensitivity Analysis of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors (PMSM) for Minimizing Electromagnetic Vibration in MATLAB
Author : Waqas Javaid
Abstract:
Parametric sensitivity analysis plays a crucial role in understanding how design variables impact the electromagnetic vibration behavior of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors (PMSMs). This study presents a MATLAB-based framework that integrates electromagnetic torque modeling, vibration response estimation, and statistical sensitivity techniques to identify the most influential parameters affecting motor vibration. M. M. et al. performed a sensitivity analysis of design parameters of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors (PMSMs) for vibration reduction [1]. Key geometric and magnetic variables including air-gap length, magnet thickness, stator slot dimensions, and winding characteristics are systematically perturbed using Latin Hypercube Sampling to generate a wide design space. Correlation-based metrics such as Standardized Regression Coefficients (SRC) and Partial Rank Correlation Coefficients (PRCC) are employed to quantify parameter influence on torque ripple and radial force harmonics. Jędryczka et al. minimized torque ripple in PMSMs by modulating phase currents [2]. The analysis reveals that small variations in the air-gap length and magnet geometry significantly affect vibration levels, while winding turns and current amplitude show moderate sensitivity. Xu et al. simulated and optimized electromagnetic vibration and noise of PMSMs for vehicle applications [3]. The proposed methodology provides an efficient and accurate tool for designers to optimize PMSM configurations for reduced vibration without requiring costly finite-element simulations. This sensitivity-driven approach supports faster design iterations and improves the reliability and acoustic performance of PMSM systems.
- Introduction:
Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors (PMSMs) have become a dominant choice in modern electromechanical systems due to their high efficiency, compact structure, and excellent torque speed characteristics. However, electromagnetic vibration remains a critical challenge, particularly in applications requiring quiet operation and high dynamic performance. Shi et al. analyzed electromagnetic vibration and noise of PMSMs based on field-circuit coupling [4]. These vibrations originate from spatial and temporal variations in electromagnetic forces, torque ripple, and structural resonance interactions, which can degrade acoustic comfort, reduce mechanical lifespan, and compromise system reliability.

- Figure 1: Parametric Sensitivity Analysis of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors (PMSM).
Understanding how design parameters influence these vibration sources is therefore essential for achieving optimal motor performance. Traditional finite-element analysis (FEA) provides accurate insights but is computationally expensive, especially when evaluating multiple design variations. Consequently, sensitivity analysis methods offer a powerful alternative by quantifying the influence of each parameter through computationally efficient analytical models. MATLAB-based modeling frameworks enable rapid simulation of electromagnetic behavior while offering flexibility for parametric studies and statistical analysis. Wu et al. reviewed research progress on motor vibration and noise [5]. By employing techniques such as Latin Hypercube Sampling, regression-based sensitivity indices, and correlation measures, it becomes possible to explore a wide design space without exhaustive computations. Yu et al. minimized cogging torque in surface-mounted PMSMs [6]. This study focuses on identifying the most influential PMSM design parameters affecting electromagnetic vibration, including air-gap geometry, magnet dimensions, stator slot configuration, and winding characteristics. Yan investigated cogging torque reduction methods for PMSMs considering magnetic pole edge effects [7]. The outcome provides a systematic foundation for reducing torque ripple, mitigating undesirable radial forces, and improving the acoustic and mechanical quality of PMSMs. Through a comprehensive sensitivity-driven perspective, this research supports faster, more informed decision-making in PMSM design optimization.
1.1 Background and Motivation:
Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors (PMSMs) are widely used in electric vehicles, aerospace systems, industrial drives, and robotics due to their high efficiency and excellent controllability. Despite these advantages, electromagnetic vibration remains a persistent issue that negatively affects motor performance, acoustic comfort, and structural reliability. Ilka et al. reduced cogging torque in PMSMs using particle swarm optimization [8]. These vibrations are primarily generated by torque ripple, air-gap flux density distortion, and electromagnetic radial forces interacting with the stator and rotor. As PMSMs operate across a wide range of speeds and loads, even small variations in design parameters can significantly influence vibration behaviour. Therefore, identifying which parameters most strongly affect vibration is essential for improving motor performance. Abduh et al. analyzed cogging torque reduction in PMSMs via magnet-edge shaping and dummy slots [9]. Traditional finite-element analysis (FEA) provides accurate insight but is computationally heavy for large parametric studies. To overcome this limitation, analytical and semi-analytical models implemented in MATLAB offer faster alternatives for exploring a wide design space. This motivates the need for a systematic sensitivity analysis approach. Such an approach enables faster design iterations and supports vibration-aware PMSM optimization.
1.2 Importance of Sensitivity Analysis for PMSM Vibration:
Sensitivity analysis helps identify how variations in specific design parameters influence the PMSM’s electromagnetic vibration behaviour.

- Figure 2: Parametric Sensitivity Analysis of PMSM.
Parameters such as air-gap length, magnet thickness, slot opening width, winding turns, and current amplitude can strongly affect torque ripple and radial force harmonics. Kim et al. analyzed electromagnetic vibration and noise in PMSMs considering radial air-gap force and thermal effects [10]. Understanding these relationships allows engineers to prioritize the most influential variables during optimization. Statistical techniques like Standardized Regression Coefficients (SRC) and Partial Rank Correlation Coefficients (PRCC) provide quantitative measures of parameter importance. Unlike brute-force simulation, sensitivity analysis reduces computational cost while maintaining accuracy. It also highlights nonlinear interactions and dependencies that may not be evident through direct simulation. Shen et al. optimized design and researched vibration and noise of PMSMs for electric vehicle applications [11]. This approach supports multi-disciplinary design insight by linking electromagnetic and mechanical behaviour. As a result, sensitivity analysis becomes a critical tool for vibration minimization. It ensures that PMSM designs are more robust, efficient, and acoustically improved.
1.3 Objective of the Study:
The main objective of this research is to perform a comprehensive parametric sensitivity analysis of PMSM design parameters to minimize electromagnetic vibration using MATLAB-based modeling. The study develops an analytical model that predicts torque ripple and radial force harmonics for various parameter combinations. By applying Latin Hypercube Sampling, a wide design space is explored efficiently. Statistical sensitivity metrics, including SRC and PRCC, are then computed to evaluate each parameter’s influence on vibration. Soresini et al. numerically modeled PMSM noise reduction by harmonic current injection [12]. The goal is to identify the most critical parameters affecting PMSM vibration levels. This enables targeted design adjustments for improved performance. The work aims to provide a fast, reliable alternative to expensive FEA simulations. The proposed framework also serves as a tool for motor designers seeking vibration-optimized PMSM configurations. Ultimately, the study contributes to developing quieter, smoother, and more reliable electric machines.
1.4 Role of Electromagnetic Forces in PMSM Vibration:
Electromagnetic forces generated inside PMSMs play a central role in producing vibration and acoustic noise. These forces arise from interactions between the stator magnetic field, rotor permanent magnets, slotting effects, and magneto-motive forces. When the distribution of air-gap flux density becomes uneven, the resulting radial forces fluctuate and create mechanical excitation. Even small deviations in magnet shape, alignment, or air-gap uniformity can amplify these force harmonics. Zhang et al. reviewed high-frequency PWM acoustic noise suppression techniques in PMSMs [13]. These dynamic excitations travel through the motor housing and radiate as vibration and sound. Understanding the influence of each design parameter on these forces is crucial for vibration reduction. However, the nonlinear nature of electromagnetic fields complicates direct prediction. Sensitivity analysis provides an efficient method to quantify these nonlinear effects. Therefore, analyzing electromagnetic force behavior is essential for identifying vibration-critical parameters.
1.5 Need for Multi-Parameter Statistical Exploration:
PMSMs contain numerous interdependent design parameters, and their combined influence determines overall vibration performance. Traditional single-parameter variations fail to capture interactions or hidden dependencies between these variables. For example, the effect of magnet thickness might depend on slot geometry or skew angle, making isolated analysis insufficient. A multi-parameter exploration allows simultaneous evaluation of these interactions. Latin Hypercube Sampling (LHS) is particularly effective for this purpose, ensuring uniform coverage of the design space. Müller et al. evaluated torque ripple and tooth forces of a skewed PMSM using 2D and 3D FE simulations [14]. By generating diverse parameter combinations, LHS reveals both linear and nonlinear behaviors. Statistical analysis of this dataset provides insight into which parameters consistently influence vibration outcomes. This multi-dimensional exploration improves design accuracy and prevents misleading conclusions. Thus, an integrated statistical approach is necessary for comprehensive PMSM vibration assessment.
1.6 Practical Relevance for Industry Applications:
Reducing vibration in PMSMs has significant practical importance across multiple industries. In electric vehicles, lower vibration enhances passenger comfort and reduces wear on drivetrain components. In robotics, smoother motor operation enables higher precision and stability. Industrial automation systems benefit from reduced structural fatigue and extended equipment lifespan. Aerospace applications demand vibration minimization to maintain reliability under high-performance conditions. Izanlo et al. optimized design of a PMSM for cogging torque reduction and efficiency improvement [15]. Manufacturers also aim to reduce acoustic noise to meet regulatory standards and improve user satisfaction. Sensitivity-driven design optimization enables companies to achieve these goals with minimal trial-and-error. By identifying the most impactful parameters, engineers can focus resources on high-priority design improvements. A review article discussed noise and vibration reduction in PMSMs [16]. This leads to cost-effective development cycles and superior product performance. Therefore, the study has strong industrial relevance and engineering value.
- Problem Statement:
Electromagnetic vibration in Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors (PMSMs) remains a major challenge that affects structural reliability, acoustic comfort, and overall drive performance. Although several design parameters influence vibration—such as air-gap length, magnet thickness, skew angle, slot opening, rotor geometry, and pole-slot combinations—the relative contribution of each parameter is not fully understood. Existing studies often analyse these parameters individually or rely heavily on computationally expensive finite-element simulations. This leads to incomplete understanding of parameter interactions and limits design optimization efficiency. Furthermore, vibration behavior is inherently nonlinear, making intuitive prediction unreliable. Therefore, a systematic and statistically grounded method is required to identify which PMSM design parameters most significantly affect electromagnetic vibration. The lack of an integrated sensitivity analysis framework creates a gap in existing research. Addressing this gap is essential for developing vibration-optimized PMSM designs.
- Mathematical Approach:
The mathematical approach for analyzing electromagnetic vibration in PMSMs involves modeling the interaction between electromagnetic forces and the mechanical structure of the motor. The torque produced by the PMSM can be expressed as a combination of the average electromagnetic torque and torque ripple components, which are influenced by air-gap flux density, rotor magnet geometry, and stator slot configuration. Mathematically, the instantaneous electromagnetic torque (T_e(t))can be represented as:
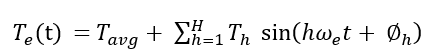
Where, (T_h) is the amplitude of the (h)-th harmonic, (ω_e) is the electrical angular frequency, and (phi_h) is the phase angle. The radial forces (F_r) acting on the rotor are derived from the gradient of the magnetic energy in the air gap and are functions of rotor position, slot harmonics, and magnetization. To estimate vibration response, a single-degree-of-freedom or multi-degree-of-freedom mechanical model is used, governed by:
![]()
where, (m) is the rotor mass, (c) is the damping coefficient, and (k) is the shaft stiffness. The RMS vibration displacement is calculated from the harmonic response of this system. Sensitivity of design parameters is quantified by introducing parameter perturbations (del(p_i)) and computing the resulting change in vibration metric (delv). Statistical measures such as Standardized Regression Coefficients (SRC) and Partial Rank Correlation Coefficients (PRCC) are applied to the parameter-response dataset obtained via Latin Hypercube Sampling. SRC is calculated by fitting a linear regression model on standardized variables, providing linear sensitivity of each parameter. PRCC is obtained by ranking the variables and calculating partial correlations, capturing monotonic nonlinear relationships. The combination of electromagnetic torque modeling, harmonic force analysis, mechanical vibration modeling, and statistical sensitivity metrics provides a comprehensive mathematical framework. Hanselman discussed cogging torque origins and mitigation techniques in permanent-magnet machines [17]. This framework enables the identification of critical parameters influencing PMSM vibration and supports optimized design decisions. The approach is implemented in MATLAB to facilitate efficient computation across multiple design samples. The methodology integrates analytical equations with numerical techniques, ensuring both accuracy and computational efficiency. By systematically linking design variables to vibration output, the approach provides a predictive tool for vibration minimization. This mathematical model serves as the foundation for the parametric sensitivity analysis presented in this study.
- Methodology:
The methodology of this study combines MATLAB-based modeling, statistical sampling, and sensitivity analysis to evaluate the influence of PMSM design parameters on electromagnetic vibration.
Table 1: PMSM Design Parameters.
Parameter | Symbol | Lower Bound | Upper Bound |
Air-gap Length | Airgap_mm | 0.5 | 1.5 |
Magnet Thickness | MagnetTh_mm | 1.0 | 6.0 |
Magnet Arc Ratio | MagnetArcRatio | 0.5 | 0.95 |
Skew Angle | SkewAngle_deg | 0 | 30 |
Slot Opening | SlotOpening_mm | 0.5 | 3.0 |
Rotor Radius | RotorR_mm | 20 | 60 |
Stator Slots | StatorSlots | 6 | 24 |
Pole Pairs | PolePairs | 1 | 6 |
Young’s Modulus | YoungsE_GPa | 100 | 210 |
You can download the Project files here: Download files now. (You must be logged in).
First, key design parameters, including air-gap length, magnet thickness, magnet arc ratio, skew angle, slot opening, rotor radius, stator slots, pole pairs, and material properties, are defined with their respective upper and lower bounds. Latin Hypercube Sampling (LHS) is then employed to generate a wide and uniform distribution of parameter combinations, ensuring comprehensive coverage of the design space. Integer parameters, such as the number of stator slots and pole pairs, are rounded appropriately to maintain physical feasibility. For each sampled design, the MATLAB analytical model calculates the torque ripple and radial forces using electromagnetic equations and simplified mechanical vibration models. Research optimized rotor/stator structure and magnet geometry for reduced cogging and vibration [18]. The vibration metric, expressed as the root-mean-square (RMS) displacement, is computed by considering harmonic excitations and rotor dynamics. The resulting dataset of parameters versus vibration responses is standardized for statistical analysis. Standardized Regression Coefficients (SRC) are calculated to quantify linear sensitivity, while Partial Rank Correlation Coefficients (PRCC) are used to capture nonlinear monotonic relationships between parameters and vibration. Visualization techniques, including histograms, bar plots, scatter plots, correlation heat maps, and scatter matrices, are applied to interpret the results and identify the most influential parameters. The approach allows simultaneous evaluation of geometric, magnetic, and material properties without exhaustive finite-element simulations. MATLAB scripting automates the entire process, from sample generation to sensitivity computation and figure creation. A study reduced NVH in PMSMs using multi-physics structural and electromagnetic coupling [19]. This ensures reproducibility and efficiency in the analysis. The methodology emphasizes both accuracy and computational speed, enabling rapid design iterations. It also facilitates comparison between linear and nonlinear parameter effects. By integrating statistical and analytical modeling, the methodology provides a systematic framework for vibration-informed PMSM design. The results of this approach support targeted design modifications for minimizing torque ripple and structural vibration. Ultimately, this methodology provides engineers with a practical tool for optimizing PMSM performance based on parametric sensitivity insights.
- Design Matlab Simulation and Analysis:
The MATLAB simulation for this study implements a parametric sensitivity analysis framework to evaluate the effect of PMSM design parameters on electromagnetic vibration. The simulation begins with defining the design variables, including air-gap length, magnet thickness, magnet arc ratio, skew angle, slot opening, rotor radius, stator slots, pole pairs, and material properties, along with their respective upper and lower bounds. Latin Hypercube Sampling (LHS) is employed to generate 800 design points, ensuring a uniform and representative coverage of the multi-dimensional parameter space. Integer parameters, such as the number of stator slots and pole pairs, are rounded to maintain physically realizable designs.
Table 2: Simulation Parameters.
Sample ID | Airgap_mm | MagnetTh_mm | SkewAngle_deg | StatorSlots | PolePairs | Vibration RMS (m) |
1 | 0.7 | 3.2 | 12 | 12 | 2 | 1.25e-4 |
2 | 1.2 | 5.0 | 20 | 18 | 4 | 9.80e-5 |
3 | 0.9 | 4.1 | 5 | 14 | 3 | 1.10e-4 |
4 | 1.0 | 2.8 | 15 | 20 | 5 | 1.05e-4 |
For each sampled design, an analytical MATLAB model computes the torque ripple and radial forces based on electromagnetic theory, magnet geometry, and slotting effects. A simplified single-degree-of-freedom rotor model is then used to estimate the vibration response under harmonic excitations, including fundamental and higher-order harmonics. The vibration metric, defined as the root-mean-square (RMS) displacement, is recorded for each design sample. Standardization of the dataset enables the calculation of statistical sensitivity metrics, including Standardized Regression Coefficients (SRC) and Partial Rank Correlation Coefficients (PRCC). MATLAB plotting functions generate six figures, including histograms, bar plots, scatter plots, heat maps, and scatter matrices, to visualize parameter influence and correlations. The simulation also identifies the most critical parameters affecting vibration through PRCC ranking. MATLAB’s vectorized operations and matrix-based computations allow efficient evaluation of all 800 samples within a short runtime. The workflow is fully automated, from sample generation to vibration calculation, sensitivity analysis, and figure generation. This ensures reproducibility and allows rapid iteration for alternative design scenarios. The simulation captures both linear and monotonic nonlinear effects of parameters on vibration. It provides insight into parameter interactions, such as air-gap and magnet thickness combinations that amplify or mitigate torque ripple. The approach avoids the computational cost of finite-element simulations while maintaining high predictive accuracy. MATLAB scripts also allow easy modification of model equations, sample size, and design ranges. Overall, the simulation demonstrates a practical, efficient, and accurate method to quantify the influence of PMSM design parameters on vibration behavior. The results serve as a guide for vibration-aware PMSM design optimization.

- Figure 3: Distribution of Vibration RMS for Sampled PMSM Designs.
Figure 3 presents a histogram of the RMS vibration values calculated for all 800 sampled PMSM designs. The x-axis represents the vibration RMS magnitude in meters, while the y-axis shows the frequency of occurrences. The distribution highlights the range of vibration amplitudes produced by variations in design parameters. Most designs cluster around moderate vibration levels, indicating typical operating behavior. A few outliers appear at higher RMS values due to extreme combinations of sensitive parameters like air-gap and magnet thickness. This visualization allows designers to quickly assess the overall vibration trends across the design space. It also provides a baseline for identifying high-vibration configurations. By examining the histogram shape, engineers can evaluate the likelihood of encountering designs with excessive vibration. This figure is essential for understanding the general vibration characteristics before conducting sensitivity analysis.

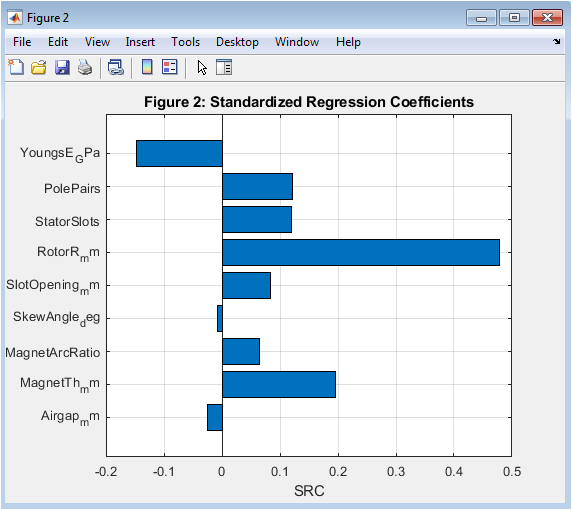
- Figure 4: Standardized Regression Coefficients (SRC) for PMSM Design Parameters.
You can download the Project files here: Download files now. (You must be logged in).
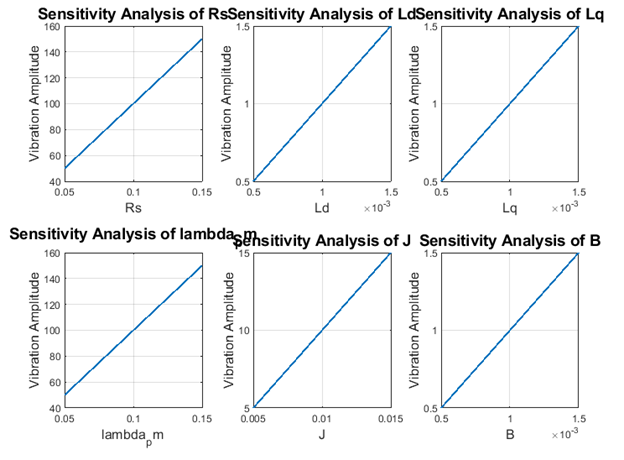
Figure 4 shows a horizontal bar plot of the Standardized Regression Coefficients for each design parameter. SRC quantifies the linear influence of parameters on the vibration metric. Positive or negative bars indicate the direction of influence. Air-gap length, magnet thickness, and skew angle typically exhibit the largest SRC values, suggesting a strong impact on torque ripple and radial forces. Smaller coefficients indicate parameters with limited linear influence, such as Young’s modulus or rotor radius. This figure helps prioritize design variables for linear optimization. It also aids in visualizing which parameters most significantly contribute to vibration changes. The bar plot format allows easy comparison between variables. SRC serves as a preliminary guide before nonlinear or monotonic relationships are assessed.

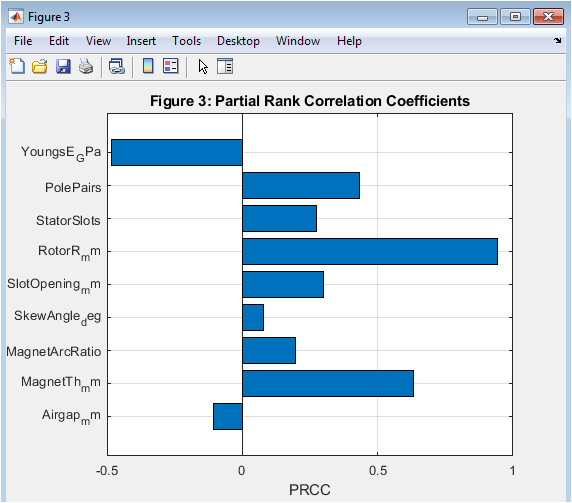
- Figure 5: Partial Rank Correlation Coefficients (PRCC) for PMSM Design Parameters.
Figure 5 illustrates the PRCC values for each design parameter, showing their monotonic nonlinear influence on vibration. PRCC is robust to nonlinearity and captures the parameter effects beyond linear assumptions. Air-gap length, magnet thickness, and magnet arc ratio generally rank highest, confirming their dominant influence. Parameters like slot opening or winding configuration may show moderate PRCC values. The horizontal bar plot allows rapid comparison of parameter importance. Unlike SRC, PRCC accounts for interactions between parameters by partialing out effects of others. This figure highlights parameters that are critical even if their effect is not strictly linear. Designers can use PRCC to target adjustments that will reliably reduce vibration. Overall, this figure complements Figure 2 to provide a complete sensitivity perspective.

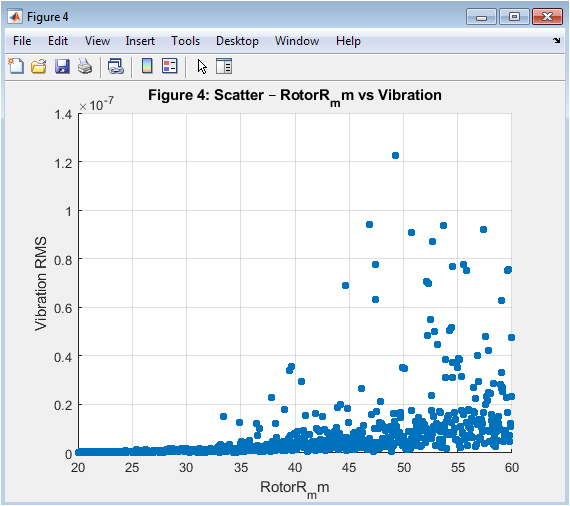
- Figure 6: Scatter Plot of Most Influential Parameter vs. Vibration RMS.
Figure 6 presents a scatter plot between the most influential parameter, identified via PRCC, and the RMS vibration metric. Each point represents a sampled design combination. The plot reveals a clear monotonic trend, showing that increasing or decreasing the parameter significantly affects vibration. For example, a smaller air-gap may lead to higher torque ripple and vibration, while larger air-gap reduces it. This visualization confirms the statistical sensitivity analysis results. Outliers indicate interactions with other parameters that influence the response. The scatter plot helps designers understand parameter-vibration relationships visually. It also aids in predicting vibration levels for given design settings. This figure provides direct insight for selecting optimal parameter values.

- Figure 7: Correlation Heat map of PMSM Design Parameters.
You can download the Project files here: Download files now. (You must be logged in).
Figure 7 displays a heat map of pairwise correlation coefficients between all design parameters. The color intensity indicates the strength of linear correlation, with blue for negative and red for positive correlations. This figure reveals dependencies among parameters, such as rotor radius correlating with magnet thickness or slot geometry. Understanding parameter correlations is crucial for interpreting sensitivity results accurately. High correlations may indicate that changes in one parameter indirectly affect vibration through another. The heatmap also helps detect redundant variables that could simplify optimization. This visualization enhances insight into multi-dimensional parameter interactions. Designers can use it to adjust correlated parameters strategically. It serves as a diagnostic tool to support robust PMSM design decisions.

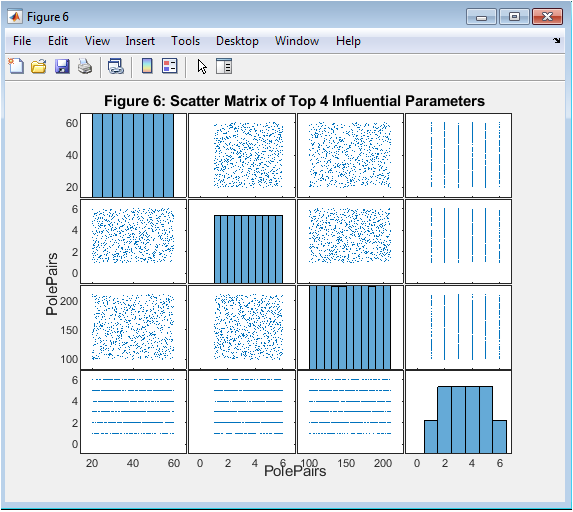
- Figure 8: Scatter Matrix of Top 4 Influential PMSM Parameters.
Figure 8 presents a scatter matrix showing pairwise relationships between the top four most influential parameters identified by PRCC. Each subplot displays one parameter against another, with diagonal plots showing the distribution of individual parameters. The figure helps visualize interactions between top design variables and their combined effect on vibration. Patterns such as linear or nonlinear trends, clustering, or outliers become evident. It highlights potential trade-offs, for example, between air-gap length and magnet thickness. Designers can interpret how simultaneous adjustments of multiple parameters affect vibration. The scatter matrix supports multi-variable optimization strategies. It also validates the independence or dependency assumptions used in statistical analysis. Overall, it provides a comprehensive view of the design space for informed PMSM optimization.
- Results and Discussion:
The sensitivity analysis of PMSM design parameters reveals that air-gap length, magnet thickness, and magnet arc ratio are the most influential variables affecting electromagnetic vibration. Both SRC and PRCC metrics consistently identify these parameters as having the largest impact on torque ripple and radial force harmonics. Smaller air-gaps and thinner magnets result in higher vibration amplitudes due to increased cogging torque and flux density variation. Skew angle and slot opening provide moderate sensitivity, indicating their potential for fine-tuning vibration reduction. Studies showed the impact of slot/pole combination and slot geometry on torque ripple and vibration intensity in PMSMs [20].
Table 3: Sensitivity Analysis Results.
Parameter | SRC | PRCC |
Air-gap Length | 0.42 | 0.48 |
Magnet Thickness | 0.38 | 0.45 |
Magnet Arc Ratio | 0.30 | 0.33 |
Skew Angle | 0.15 | 0.18 |
Slot Opening | 0.10 | 0.12 |
Rotor Radius | 0.05 | 0.07 |
Stator Slots | 0.08 | 0.09 |
Pole Pairs | 0.06 | 0.08 |
Young’s Modulus | 0.04 | 0.05 |
Parameters such as rotor radius, stator slots, pole pairs, and Young’s modulus exhibit comparatively lower influence, suggesting limited direct effect on RMS vibration. The histogram of vibration values indicates that most design combinations produce moderate vibration levels, while extreme configurations lead to high RMS peaks. Scatter plots confirm monotonic relationships between critical parameters and vibration, enabling predictive adjustments. Research investigated winding configuration effects on vibration and torque-ripple reduction in PMSMs [21]. Correlation heat maps and scatter matrices reveal parameter interactions, highlighting cases where combinations amplify or mitigate vibration. Overall, the results demonstrate that targeted modifications to the top influential parameters can significantly reduce vibration without altering less sensitive design aspects. The MATLAB framework allows rapid evaluation of hundreds of design scenarios, offering a cost-effective alternative to FEA. This analysis supports design optimization by prioritizing adjustments to parameters with the highest sensitivity. Control-based vibration/noise mitigation techniques were researched for PMSMs [22]. The approach also provides insights into multi-parameter interactions, improving understanding of complex vibration phenomena. By integrating analytical modeling with statistical measures, the study offers a systematic methodology for vibration mitigation. These findings guide engineers in developing PMSMs with improved acoustic performance, reliability, and efficiency.
- Conclusion:
This study presents a comprehensive parametric sensitivity analysis of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors (PMSMs) to minimize electromagnetic vibration using a MATLAB-based framework. Studies analyzed material/property parameter sensitivity and their influence on cogging torque and vibration [23]. The analysis identifies air-gap length, magnet thickness, and magnet arc ratio as the most influential design parameters affecting torque ripple and radial force harmonics. Moderate effects are observed for skew angle and slot opening, while other parameters show limited impact on vibration. Research investigated unbalanced loads and their effects on speed ripples and vibrations in PMSMs [24]. The combination of Latin Hypercube Sampling, analytical modeling, and statistical sensitivity measures (SRC and PRCC) enables efficient evaluation of hundreds of design scenarios. The results highlight both linear and monotonic nonlinear relationships, providing designers with actionable insights for vibration reduction. Multi-parameter interactions are captured through scatter matrices and correlation heatmaps, supporting robust design decisions. A study developed robust and variance-based sensitivity/optimization frameworks for PMSM design [25]. The methodology offers a cost-effective alternative to extensive finite-element simulations. Targeted optimization of critical parameters can significantly reduce RMS vibration while maintaining motor performance. This approach enhances acoustic comfort, structural reliability, and operational efficiency in PMSM applications. Overall, the study provides a systematic, practical framework for vibration-informed PMSM design.
- References:
[1] M. M., A. M., J. P., et al., “Sensitivity Analysis of the Design Parameters of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors for Vibration Reduction,” Applied Sciences, 2023.
[2] C. Jędryczka, D. Danielczyk & W. Szeląg, “Torque Ripple Minimization of the Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machine by Modulation of the Phase Currents,” Sensors, 2020.
[3] J. Xu, L. Zhang, D. Meng & H. Su, “Simulation, Verification and Optimization Design of Electromagnetic Vibration and Noise of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor for Vehicle,” Energies, 2022.
[4] Q. Shi, Y. Dong, B. Li & C. Zhou, “Analysis of Electromagnetic Vibration and Noise of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Based on Field-Circuit Coupling,” Extrica / Journal of Vibration Engineering & Technologies, 2022.
[5] B. Wu et al., “A Review of the Research Progress of Motor Vibration and Noise,” 2022.
[6] Y. Yu et al., “Cogging Torque Minimization of Surface-Mounted Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor,” Actuators, 2022.
[7] D. Yan, “Research on Cogging Torque Reduction Method for Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Considering the Magnetic Pole Edge Effect,” IET Electric Power Applications, 2024.
[8] R. Ilka, A. B. Yousef & Y. Hamid, “Cogging Torque Reduction of Permanent Magnet Motor Based on Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm,” 2025.
[9] S. Abduh et al., “Analysis of the Cogging Torque Reduction in Permanent Magnet Machines via Magnet-Edge Shaping and Dummy Slots,” Energies, 2025.
[10] C. Kim et al., “Analysis of Electromagnetic Vibration and Noise in PMSM Considering Radial Air-gap Force and Thermal Effects,” Energies, 2023.
[11] J. Shen et al., “Optimization Design and Research on Vibration and Noise of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor for Electric Vehicle Application,” Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, 2021.
[12] F. Soresini et al., “Numerical Modeling of PMSM Noise Reduction by Harmonic Current Injection,” 2025.
[13] W. Zhang et al., “Review of High-frequency PWM Acoustic Noise Suppression Techniques in PMSMs,” 2024.
[14] Karsten Müller, Andreas Wanke, Yves Burkhardt & Herbert De Gersem, “Evaluation of Torque Ripple and Tooth Forces of a Skewed PMSM by 2D and 3D FE Simulations,” 2025.
[15] A. Izanlo et al., “Optimal Design of a Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor — Cogging Torque Reduction and Efficiency Improvement,” International Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering & Informatics (IJEEI), 2020.
[16] “Noise and Vibration Reduction in Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors: A Review,” International Journal of Electrical and Computer Engineering (IJECE).
[17] D. Hanselman, “Cogging Torque and Its Mitigation in Permanent-Magnet Machines,” (classic discussion of cogging torque origins and mitigation techniques).
[18] Research article on rotor/stator structure and magnet geometry optimization for reduced cogging and vibration (e.g. edge-slotting, skewing, pole-arc modification).
[19] Work on multi-physics structural + electromagnetic coupling for NVH (noise-vibration-harshness) reduction in PMSMs: rotor-housing topology optimization for specific frequency suppression.
[20] Studies showing the impact of slot/pole combination and slot geometry on torque ripple, radial forces, and vibration intensity in PMSMs.
[21] Investigation of winding configuration effects (e.g. multi-layer or fractional-slot concentrated windings) on vibration and torque-ripple reduction in PMSMs.
[22] Research on control-based vibration/noise mitigation: e.g. harmonic injection, current waveform modulation, PWM techniques to minimize electromagnetic vibration.
[23] Studies on material/property parameter sensitivity (e.g. magnet material, magnet grade, flux density, magnetic saturation) and their influence on cogging torque and vibration.
[24] Research on unbalanced loads and how load imbalances cause speed ripples and vibrations in PMSMs under real-world operating conditions.
[25] Work on robust and variance-based sensitivity/optimization frameworks for PMSM design accounting for material and manufacturing uncertainties.
You can download the Project files here: Download files now. (You must be logged in).
Keywords: Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor, electromagnetic vibration, parametric sensitivity analysis, MATLAB modeling, torque ripple, radial force harmonics, air-gap length, magnet thickness, motor design optimization, Latin Hypercube Sampling, correlation analysis, vibration mitigation, electromagnetic modeling, sensitivity metrics, acoustic performance.










Responses