Discovering Matlab: Top 10 Productivity Tools

When it comes to data analysis, numerical computation, and algorithm development, MATLAB stands as one of the most powerful and versatile tools available to researchers, engineers, and scientists. With its extensive library of built-in functions and user-friendly interface, MATLAB enables users to tackle complex problems with ease. In this article, we will explore the top 10 productivity tools within MATLAB that can supercharge your workflow and enhance your productivity. So, let’s dive in!
MATLAB Editor
The MATLAB Editor is a feature-packed integrated development environment (IDE) that provides a comprehensive set of tools for writing, editing, and debugging code. With syntax highlighting, automatic code indentation, and smart code suggestions, the MATLAB Editor boosts your coding productivity and minimizes errors. Take advantage of its integrated debugger to identify and resolve issues quickly, ensuring the smooth execution of your scripts and functions.
MATLAB Live Editor
The Live Editor in MATLAB takes interactivity to a whole new level. It combines code, text, and visualizations in a single environment, allowing you to create live scripts and documents. With the ability to evaluate code snippets on the fly, the Live Editor facilitates rapid prototyping, experimentation, and documentation. Use it to generate reports, share your findings, and collaborate with others seamlessly.
MATLAB Parallel Computing Toolbox
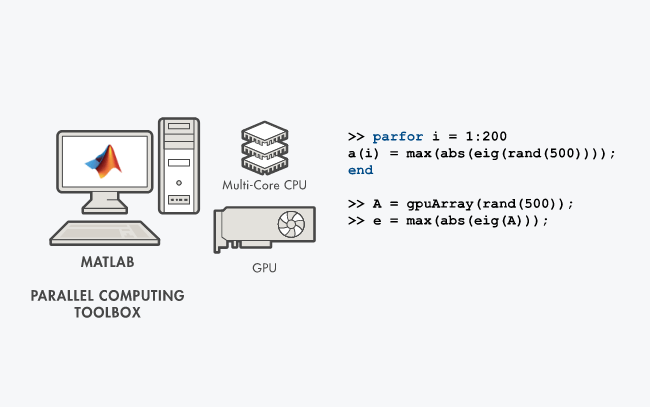
For computationally intensive tasks, the Parallel Computing Toolbox in MATLAB provides a powerful solution. Harness the potential of multicore processors, clusters, and cloud resources to accelerate your simulations, data processing, and optimization tasks. By leveraging parallel computing, you can significantly reduce the execution time of your code, allowing for faster iterations and increased productivity.
MATLAB App Designer
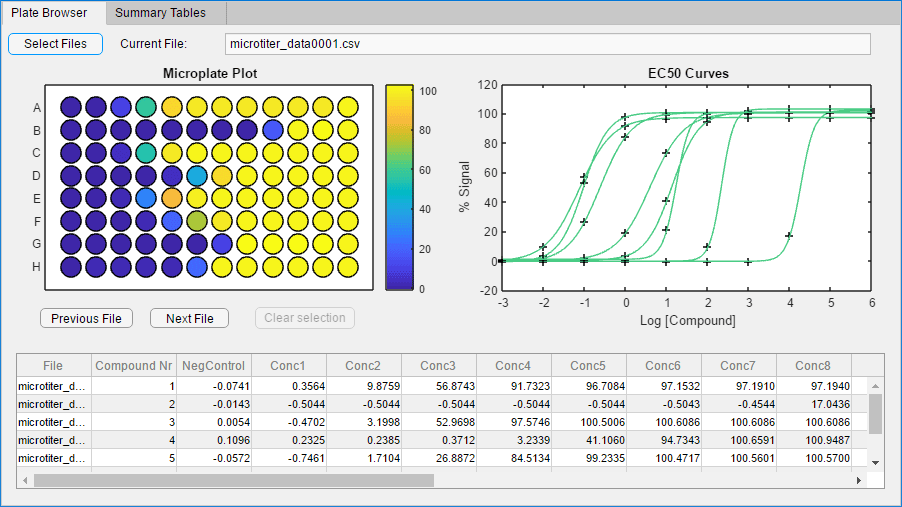
As can be seen, building graphical user interfaces (GUIs) can be a time-consuming task, but not with MATLAB’s App Designer. This drag-and-drop environment enables you to create interactive and visually appealing GUIs effortlessly. Whether you need to develop a data visualization tool or an application for data analysis, the App Designer empowers you to bring your ideas to life in a fraction of the time, reducing the development cycle and boosting productivity.
Simulink
Simulink is a powerful block diagram environment within MATLAB that allows you to model, simulate, and analyze dynamic systems. It provides a wide range of pre-built blocks for designing complex control systems, signal processing algorithms, and communication systems. With Simulink, you can visualize and fine-tune your models interactively, making it an invaluable tool for developing and testing algorithms before deployment.
Read also: Simulink – a must-have tool for signal processing
Image Processing Toolbox
Basically, for researchers and engineers working with images and computer vision, the Image Processing Toolbox in MATLAB is a game-changer. It offers a comprehensive set of functions and algorithms for image enhancement, segmentation, feature extraction, and object recognition. By leveraging these tools, you can automate image processing tasks, analyze large datasets efficiently, and gain valuable insights from visual data.
MATLAB Optimization Toolbox
Optimization problems are prevalent in various domains, ranging from engineering design to financial modeling. MATLAB’s Optimization Toolbox provides a suite of optimization algorithms and tools to solve a wide range of optimization problems. Whether you need to maximize profits, minimize costs, or find the optimal parameters for a model, the Optimization Toolbox equips you with the necessary tools to tackle complex optimization challenges effectively.
Deep Learning Toolbox
Deep learning has revolutionized the field of artificial intelligence, enabling remarkable breakthroughs in image recognition, natural language processing, and predictive modeling. MATLAB’s Deep Learning Toolbox offers a comprehensive set of functions and tools for designing, training and deploying deep neural networks. Leverage its pre-trained models or build your own to solve complex problems, accelerating your research and development efforts.
Symbolic Math Toolbox
The Symbolic Math Toolbox is a powerful tool within MATLAB that enables users to perform symbolic computations, manipulate mathematical expressions, and solve complex mathematical problems symbolically. Unlike numerical computation, which focuses on obtaining numeric results, symbolic computation deals with mathematical objects and expressions in their exact form, preserving variables, constants, and functions as symbols rather than substituting them with specific values.
Additionally, with the Symbolic Math Toolbox, users can create symbolic variables, constants, and functions. As well as perform operations on them symbolically. This allows for a more flexible and comprehensive approach to mathematical analysis. Additionally, it enables the manipulation and simplification of mathematical expressions without the need for explicit numerical values.
MATLAB Data Import and Export
MATLAB provides various tools and functions for importing and exporting data from different file formats, including spreadsheets, text files, databases, and more. These tools streamline the data processing workflow and make it easier to work with external data sources.
By leveraging these top 10 productivity tools, users can enhance their MATLAB workflows and tackle complex tasks more effectively.
In the world of data analysis and scientific research, MATLAB tools have long been heralded as a beacon of innovation and efficiency. From unraveling complex algorithms to solving intricate mathematical equations, these tools have empowered countless individuals and organizations to unlock the hidden potential of their data.













Responses