
Home » Engineering
Engineering


Integrated Water Quality Monitoring System with Sensor Fusion, Anomaly Detection, and WQI Prediction Using Matlab
waqas javaid 13. February 2026
Read More »
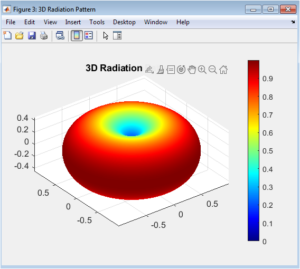
Numerical Modeling and 3D Visualization of Dipole Antenna Radiation Patterns Using MATLAB
waqas javaid 13. February 2026
Read More »
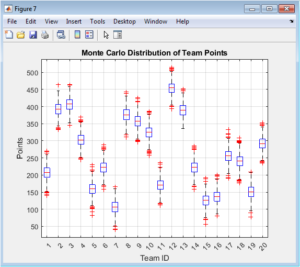
Advanced Statistical Modeling of Team and Player Performance in Competitive Sports Using Matlab
waqas javaid 13. February 2026
Read More »
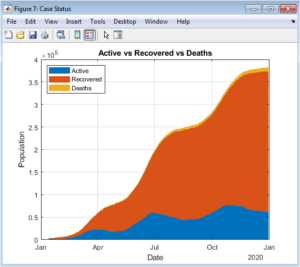
An Advanced MATLAB-Based Visualization Framework for Multi-Wave COVID-19 Pandemic Trend Analysis
waqas javaid 13. February 2026
Read More »

Implementation and Evaluation of a Text Sentiment Analyzer using MATLAB and Machine Learning
waqas javaid 13. February 2026
Read More »
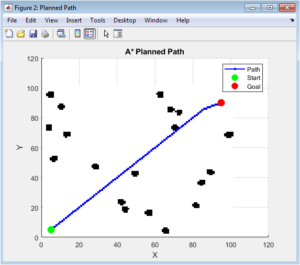
A MATLAB Simulation Platform for Testing Autonomous Navigation Algorithms in Dynamic Environments
waqas javaid 13. February 2026
Read More »
Design and Simulation of a 6-DoF (Degree-of-Freedom) Drone PID Flight Controller in MATLAB
waqas javaid 13. February 2026
Read More »
Earthquake Detection and Analysis Using Seismic Signal Processing in Matlab
waqas javaid 13. February 2026
Read More »

Design and Implementation of a Digital Communication System Simulator using MATLAB
waqas javaid 13. February 2026
Read More »







