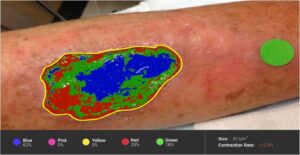
Abstract — This work investigates the leader-follower formation control of multi-robot systems, an important field in robotics with broad applications in agriculture, logistics, and surveillance. The work illustrates the efficacy of geometric, potential field, and behavior-based control techniques in producing and sustaining desirable shapes through a thorough implementation utilizing the Turtlesim simulator in ROS. The technological difficulties posed by dynamic and unstructured environments are discussed, emphasizing the ongoing need for advancements in coordination and control algorithms [2] [3]. This work critically assesses the ethical ramifications of using autonomous robots in larger social contexts, going beyond their technical limitations. Safeguarding privacy to preserve sensitive data, removing algorithmic bias to ensure fairness, addressing the socioeconomic effects of potential employment displacement, and assuring safety to prevent accidents are among the main challenges [5]. The project intends to pave the road for the responsible and sustainable integration of these technologies into society, ensuring they contribute positively while reducing potential negative effects, by including ethical considerations into the design and deployment of autonomous robots.
Keywords — autonomous robots, geometric control, multi-robot systems, ROS, Turtlesim, algorithmic bias, safety, privacy, ethical concerns, urban deployment, autonomous navigation, robotic coordination, leader-follower formation control.
 Circuit analysis has long been a traditional introduction to the art of problem solving from an engineering perspective, even for those whose interests lie outside electrical engineering.
Circuit analysis has long been a traditional introduction to the art of problem solving from an engineering perspective, even for those whose interests lie outside electrical engineering.